It may be costly to treat chronic diseases. The remote monitoring of patients is an effective tool that can help promote patients' participation in the effective management of chronic diseases. Traditionally, patients have been tasked with keeping track of their physiological measurements, writing them down, waiting for an appointment, and then sending their readings by hand to their doctor. This cumbersome process is fraught with potential errors and significant risks of non-compliance.
The remote monitoring of patients simplifies the process by providing the opportunity to bring the management of various chronic diseases into modern times. These portable, easy-to-use connected devices can play a positive role in their treatment plans. By participating more regularly, doctors can help patients make greater long-term progress and reduce avoidable costly treatments.
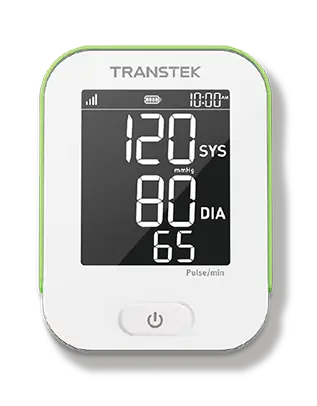
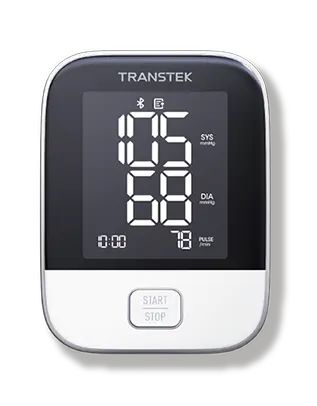
Hypertension: with remote blood pressure monitoring, patients and providers can view trends and acute blood pressure readings in real time. After that, healthcare providers can classify patients who may be close to a hypertension crisis. In addition, they can know when to contact patients who may benefit from long-term blood pressure management. Studies have shown that improved blood pressure control can significantly reduce cardiovascular risk, 20 to 25 percent for heart attack, 35 to 40 percent for stroke, and 50 percent for heart failure. The remote monitoring of patients improves blood pressure control, reduces the need for blood pressure medications and decreases the inertia of medication administration.
Obesity: the remote monitoring of patients eliminates patients' adherence to daily weighing, records these numbers, and brings them to their provider to discuss their progress in weight loss. In addition, it integrates weight trend data into the database to make providers engage and reach out to patients who deviate from their weight goals. Studies have shown that patients who use internet-connected scales every day lose more weight. In addition, telemedicine methods such as cellphone-based tutoring and video could be useful tools to support obese patients to lose weight.
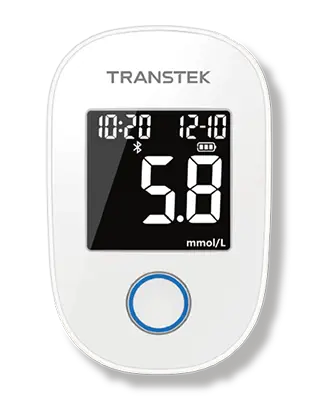
Diabetes: the remote monitoring of patients can help people with diabetes avoid acute life-threatening events and provide comprehensive long-term management of their disease. When patients check their blood sugar levels, the remote monitoring of patients can alert clinical staff to abnormally high or low readings and check with patients to avoid preventable adverse outcomes such as emergency room visits and hospitalizations. In addition, remote monitoring enables suppliers to adjust medicines through telemedicine access. Both patients and their providers can be better informed about glucose control trends and proactive in preventing the devastating long-term complications of the disease. Some preliminary studies suggest that the remote monitoring of patients can benefit patients with type 2 diabetes after discharge from the hospital. Patients who use the devices for remote monitoring of patients at home experience improved health outcomes, including lower A1c levels.
+86-0760-85702291